Healthcare Facilities Can Protect Their Digital Asset Management (DAM) System
Digital Asset Management (DAM) has become an essential element of healthcare facilities today, from hospitals and clinics to imaging laboratories and administrative documents. DAM such as Blueberry solution involves organizing, storing, retrieving, and safeguarding digital assets like medical records, imaging files, and administrative documents - critical data must remain protected due to their sensitive nature. In this article, we explore various techniques healthcare facilities use to ensure their DAM systems remain secure such as technological measures, regulatory compliance measures as well as best practices.
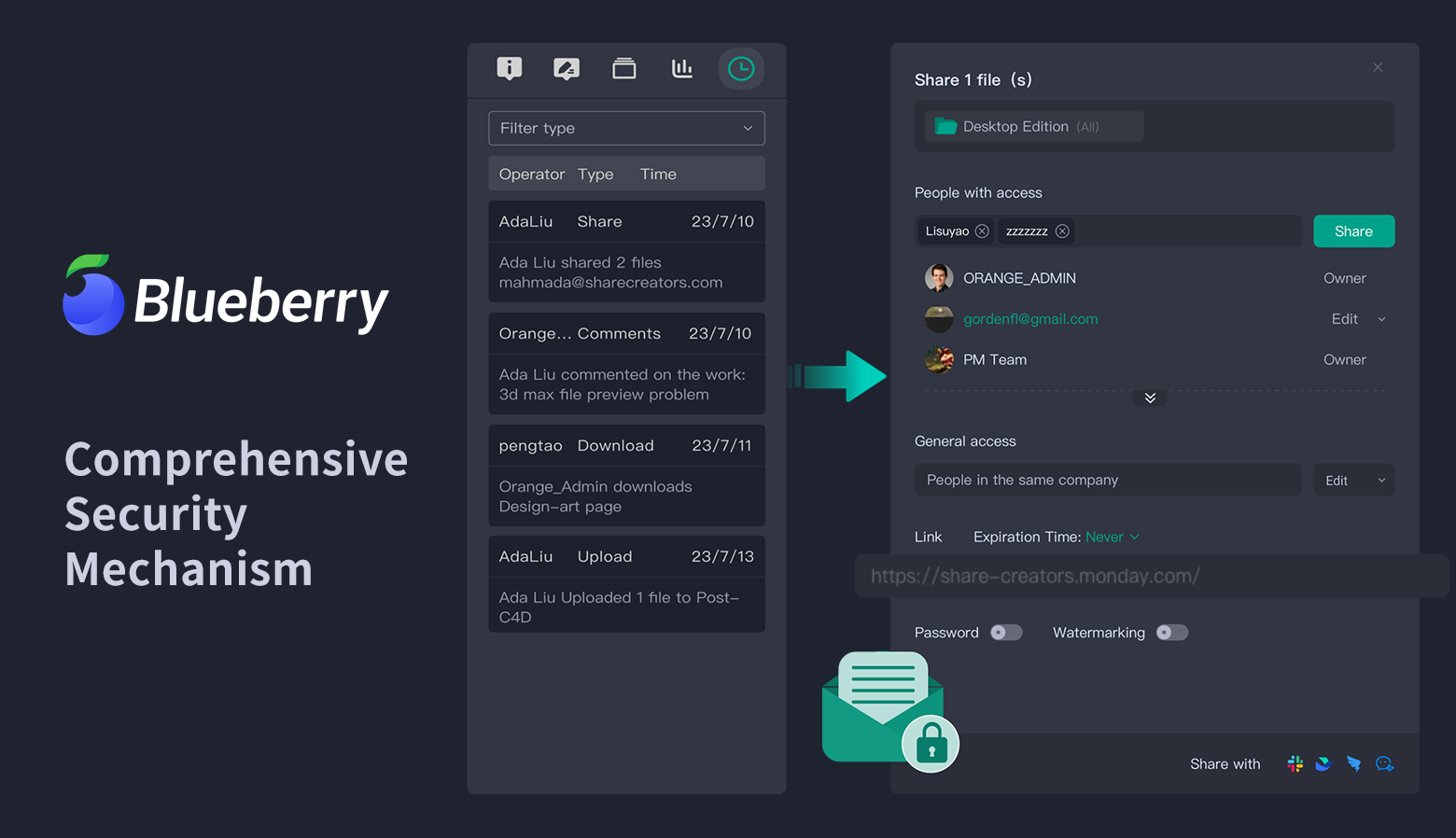
1. Robust Access Control Mechanisms
A cornerstone of DAM security lies in controlling who gains access to its contents. Healthcare facilities employ stringent access control measures designed to restrict specific digital assets to authorized personnel only - this may involve employing several strategies:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC systems restrict user access based on their role within an organization; for instance, doctors might only have access to patient medical records while administrative staff have access to scheduling details but not sensitive patient medical files.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple verification forms before access is granted to DAM systems can significantly bolster security. These typically include something the user knows (password), has (security token), or even themselves (biometric verification).
Least Privilege Principle: Ensuring users only possess access necessary for performing their jobs reduces the risk of unauthorized data access and breaches.
DAM system with robust security on sensitive assets.
2. Encryption Data encryption
This is an integral component in protecting digital assets, with healthcare facilities using encryption at rest (data stored locally on servers) and during transit over networks.
Encryption at Rest: Data stored in databases, file systems, and backup media is encrypted using strong encryption algorithms, to protect it even if someone gains unauthorized access and attempts to read without decryption keys.
Encryption-in-Transit: Data transmitted across the internet or internal networks are secured using protocols like Transport Layer Security to avoid being intercepted and read during transmission
3. Compliance With Regulatory Standards
Healthcare facilities must abide by numerous regulating standards that mandate security measures designed to safeguard patient information. Key regulations include:
HIPAA) in the U.S. sets standards for protecting sensitive patient data. Healthcare providers must implement physical, network, and process security measures.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR provides healthcare facilities operating within Europe with stringent data protection and privacy regulations and penalties should they fail to abide.
ISO/IEC 27001: This international standard specifies requirements for creating, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS).
4. Routine Security Audits and Assessments
Healthcare facilities engage in regular security audits to assess vulnerabilities within their DAM systems, identify risk areas, and mitigate vulnerabilities as quickly as possible. Audits typically include:
Internal Audits: Conducted by an in-house IT security team, internal audits analyze system configurations, access logs, and security policies to comply with internal and external standards.
External Audits: Third-party security experts often conduct impartial assessments. Such audits offer an independent view of a facility's security posture while pinpointing areas in need of improvement.
Penetration Testing: Simulated cyberattacks are conducted to test the defenses of DAM systems and identify any entry points that might be exploited by malicious actors.
5. Advanced Threat Detection and Response
Modern DAM systems in healthcare facilities come equipped with sophisticated threat detection and response mechanisms that include:
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): These security solutions monitor network traffic for any suspicious activities that could pose threats and can alert on or block potential risks immediately.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM solutions aggregate and analyze data from different sources to detect patterns indicative of potential security threats and provide real-time analysis and incident response capabilities.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These cutting-edge technologies have proven invaluable in improving threat detection by more quickly and accurately detecting anomalies or potential threats than conventional methods allow.
6. Data Backup and Recovery Plans
To safeguard digital assets, healthcare facilities implement comprehensive backup strategies to safeguard their digital assets against cyber attacks, hardware malfunction, or natural disasters. This safeguard helps prevent data loss due to hacks or disasters.
Regular Backups: Data should be regularly backed up across different locations - both offline and online storage solutions such as the cloud.
Blueberry DAM offering tight security to assets.
Disaster Recovery Plans: Careful planning ensures minimal disruption of operations and rapid restoration of services should a data breach or disaster strike, providing necessary steps for quick restoration.
7. Employee Training and Awareness
Human error can be an imminent risk when it comes to data security, so healthcare facilities invest in ongoing employee education programs on this matter to spread knowledge among staff about its importance as well as best practices.
Security Awareness Training: Conduct regular security awareness sessions covering topics like recognizing phishing attempts, password administration best practices, and the protection of sensitive data.
Simulated Phishing Campaigns: These tests measure employee responses to fake phishing emails, helping identify where additional training may be required.
8. Physical Security Measures
Healthcare facilities understand that physical security is vital when protecting digital assets, so they use measures to limit physical access to systems and storage areas containing important digital files.
Access Controls: Protect data centers and other sensitive areas using key cards, biometric scanners, and surveillance cameras with secure entry access controls.
Blueberry DAM offering comprehensive security for assets.
Environmental Controls: Protecting against environmental threats such as fire, flooding, and power outages is of critical importance; to do this effectively you need fire suppression systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs), and climate control systems in place.
9. Data Anonymization and De-identification
Healthcare facilities often utilize data anonymization and de-identification techniques to protect patient privacy further. These procedures alter data such that it cannot be linked back to individual patients thereby decreasing risks should any data breaches take place.
Anonymization: Deliberately removes personal identifying details so it's impossible for an individual to connect his or her data back to an identifiable individual.
De-Identification: Deliberately alters data by concealing identifiable details while keeping open the possibility for later re-identification using secure keys or similar methods.
10. Vendor Management
Healthcare facilities often depend on third-party vendors for various services like cloud storage, software development, and IT support; assuring they adhere to similar security standards is therefore of utmost importance.
Vendor Risk Evaluations: Conduct regular assessments of third-party vendors' security practices to ensure they adhere to both facility policies and regulatory requirements.
Contracts and SLAs: Include specific security requirements and incident response protocols into contracts and service level agreements (SLAs) with vendors.
Summary,
Digital asset security for healthcare facilities can only be ensured with an integrative, multi-layered strategy that blends technological solutions, regulatory compliance requirements, and best practices. Healthcare facilities can protect their sensitive data by employing effective access controls, encryption technologies, security audits, advanced threat detection methods, and ongoing employee training to ward off threats to sensitive information. Healthcare facilities bolster their DAM systems' security with robust backup and recovery plans, physical security measures, data anonymization, and vigilant vendor management practices that safeguard patient confidentiality while building trust among their services' patients. Through such efforts, they ensure patient information remains private while safeguarding trust within their services.
Please visit Blueberry DAM free trial for more information.